Learn how to perform server-side operations using Node.js with a complete reference implementation that uses the MySQL database.
This guide is intended as a starting point when learning how to use the Server-Side Row Model, as it provides a simple grid implementation that uses a limited set of features and grid configurations.
The sample Olympic Medals application is developed using a Node.js server that connects to a MySQL database and will demonstrate how data can be lazy-loaded as required, even when performing group, filter and sort operations when working with large datasets.
The reference implementation covered in this guide is for demonstration purposes only. If you use this in production it comes with no warranty or support.
The source code can be found here: https://github.com/ag-grid/ag-grid-server-side-nodejs-example.
Overview Copy Link
In this Olympic Medals application, the server endpoint will be hosted using a web server comprised of Node.js running Express.js, that connects to a single MySQL datasource.
An overview of technologies used in this guide is illustrated in the diagram below:
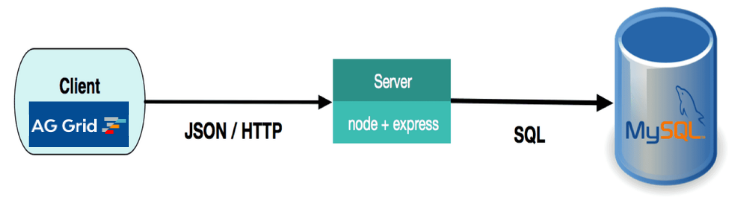
We will now proceed to install and run the application before going through the implementation details.
Download and Install Copy Link
Clone the example project using:
git clone https://github.com/ag-grid/ag-grid-server-side-nodejs-example.git
Navigate into the project directory:
cd ag-grid-server-side-nodejs-example
Install project dependencies and build project using:
yarn install
Database Setup Copy Link
Download and install the database as per the MySQL Download documentation.
Create a database with the name 'sample_data'. Then run the following script to create the table olympic_winners and populate it with data via the MySQL command line:
mysql -u root -p -D sample_data < ./data/olympic_winners.sql
That's it! We are now ready to run and explore the application.
Running the application Copy Link
To run the application execute the following from the command line:
yarn start
Then point your browser to http://localhost:4000/
Client Configuration Copy Link
In order to keep this sample application as simple as possible, the grid configuration is kept to a minimum. The gridOptions required for our grid are shown below:
// client/index.js
const gridOptions = {
rowModelType: 'serverSide',
columnDefs: [
{ field: 'athlete' },
{ field: 'country', rowGroup: true, hide: true },
{ field: 'sport', rowGroup: true, hide: true },
{ field: 'year', filter: 'number' },
{ field: 'gold', aggFunc: 'sum' },
{ field: 'silver', aggFunc: 'sum' },
{ field: 'bronze', aggFunc: 'sum' },
],
}
In the code snippet above, the grid is configured to use the Server-Side Row Model by setting: gridOptions.rowModelType = 'serverSide'.
Sorting is enabled by default. A simple number filter is also added to the 'year' column. Note that as new data is loaded the applied filters are kept.
To demonstrate Row Grouping, the 'country' and 'sport' columns have been configured with rowGroup = true. Finally, to ensure the medal values are aggregated up the group hierarchy, the value columns have been set up with an aggregation function: aggFunc='sum'.
Server-Side Datasource Copy Link
In order to fetch data for the Server-Side Row Model we must implement the IServerSideDatasource, which contains a single method getRows(params) which accepts request params from the grid.
Successful responses are then passed back to the grid via the params.successCallback(rows, lastRow) as shown below:
// client/index.js
const datasource = {
getRows(params) {
console.log(JSON.stringify(params.request, null, 1));
fetch('./olympicWinners/', {
method: 'post',
body: JSON.stringify(params.request),
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json; charset=utf-8' }
})
.then(httpResponse => httpResponse.json())
.then(response => {
params.successCallback(response.rows, response.lastRow);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error(error);
params.failCallback();
})
}
};
// register datasource with the grid
api.setGridOption('serverSideDatasource', datasource);
Server Endpoint Copy Link
Hosting our server endpoint /olympicWinners which accepts JSON requests is done with the help of the express and body-parser npm packages.
// server/server.js
import webpack from 'webpack';
import webpackMiddleware from 'webpack-dev-middleware';
import webpackConfig from '../webpack.config.js';
import express from 'express';
import bodyParser from 'body-parser';
import OlympicWinnersService from './olympicWinnersService';
const app = express();
app.use(webpackMiddleware(webpack(webpackConfig)));
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({extended: false}));
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.post('/olympicWinners', function (req, res) {
OlympicWinnersService.getData(req.body, (rows, lastRow) => {
res.json({ rows: rows, lastRow: lastRow });
});
});
app.listen(4000, () => {
console.log('Started on localhost:4000');
});
Request are delegated to the OlympicWinnersService which contains all the server-side application logic. The getData() method queries the MySQL database using the mysql npm package with the SQL returned by buildSql().
// server/olympicWinnersService.js
import mysql from 'mysql';
class OlympicWinnersService {
getData(request, resultsCallback) {
const SQL = this.buildSql(request);
connection.query(SQL, (error, results) => {
const rowCount = this.getRowCount(request, results);
const resultsForPage = this.cutResultsToPageSize(request, results);
resultsCallback(resultsForPage, rowCount);
});
}
buildSql(request) {
const selectSql = this.createSelectSql(request);
const fromSql = ' FROM sample_data.olympic_winners ';
const whereSql = this.createWhereSql(request);
const limitSql = this.createLimitSql(request);
const orderBySql = this.createOrderBySql(request);
const groupBySql = this.createGroupBySql(request);
return selectSql + fromSql + whereSql + groupBySql + orderBySql + limitSql;
}
// helper methods ...
}
The buildSql() method uses a number of helper methods to build up SQL fragments used in the combined SQL which is returned. The implementation details of these helper methods are be omitted from this guide but can be examined in the project repository.
Conclusion Copy Link
In this guide we presented a reference implementation for integrating the Server-Side Row Model with a Node.js server connected to a MySQL database. This included all necessary configuration and install instructions.
A high level overview was given to illustrate the problem this approach solves before providing details of how to achieve the following server-side operations:
- Sorting
- Filtering
- Grouping
- Aggregation