Number Filters allow you to filter numeric data.
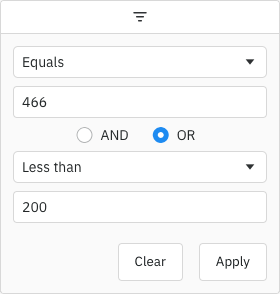
Enabling Number Filters Copy Link
The Number Filter is the default filter used in AG Grid Community for columns with number Cell Data Type, but it can also be explicitly configured as shown below:
const [columnDefs, setColumnDefs] = useState([
{
field: 'price',
// Number Filter is used by default in Community version for numeric columns
filter: true,
filterParams: {
// pass in additional parameters to the Number Filter
},
},
{
field: 'quantity',
// explicitly configure column to use the Number Filter
filter: 'agNumberColumnFilter',
filterParams: {
// pass in additional parameters to the Number Filter
},
},
]);
<AgGridReact columnDefs={columnDefs} /> Number Filter Parameters Copy Link
Number Filters are configured through the filterParams attribute of the column definition (INumberFilterParams interface):
When specified, the input field will be of type text, and this will be used as a regex of all the characters that are allowed to be typed. This will be compared against any typed character and prevent the character from appearing in the input if it does not match.
|
Specifies the buttons to be shown in the filter, in the order they should be displayed in. The options are: 'apply': If the Apply button is present, the filter is only applied after the user hits the Apply button. 'clear': The Clear button will clear the (form) details of the filter without removing any active filters on the column. 'reset': The Reset button will clear the details of the filter and any active filters on that column. 'cancel': The Cancel button will discard any changes that have been made to the filter in the UI, restoring the applied model. |
If the Apply button is present, the filter popup will be closed immediately when the Apply or Reset button is clicked if this is set to true. |
Overrides the default debounce time in milliseconds for the filter. Defaults are: TextFilter and NumberFilter: 500ms. (These filters have text field inputs, so a short delay before the input is formatted and the filtering applied is usually appropriate). DateFilter and SetFilter: 0ms |
By default, the two conditions are combined using AND. You can change this default by setting this property. Options: AND, OR
|
The default filter option to be selected. |
Array of filter options to present to the user.
|
Placeholder text for the filter textbox.
|
If true, the 'inRange' filter option will include values equal to the start and end of the range. |
If true, blank (null or undefined) values will pass the 'equals' filter option. |
If true, blank (null or undefined) values will pass the 'greaterThan' and 'greaterThanOrEqual' filter options. |
If true, blank (null or undefined) values will pass the 'lessThan' and 'lessThanOrEqual' filter options. |
If true, blank (null or undefined) values will pass the 'notEqual' filter option. |
If true, blank (null or undefined) values will pass the 'inRange' filter option. |
Maximum number of conditions allowed in the filter. |
By default only one condition is shown, and additional conditions are made visible when the previous conditions are entered (up to maxNumConditions). To have more conditions shown by default, set this to the number required. Conditions will be disabled until the previous conditions have been entered. Note that this cannot be greater than maxNumConditions - anything larger will be ignored. |
Typically used alongside allowedCharPattern, this provides a custom formatter to convert the number value in the filter model into a string to be used in the filter input. This is the inverse of the numberParser.
|
Typically used alongside allowedCharPattern, this provides a custom parser to convert the value entered in the filter inputs into a number that can be used for comparisons.
|
If set to true, disables controls in the filter to mutate its state. Normally this would be used in conjunction with the Filter API. |
Custom Number Support Copy Link
The default behaviour of the Number Filter is to use a number input, however this has mixed browser support and behaviour. If you want to override the default behaviour, or allow users to type other characters (e.g. currency symbols, commas for thousands, etc.), the Number Filter allows you to control what characters the user is allowed to type. In this case, a text input is used with JavaScript controlling what characters the user is allowed (rather than the browser). You can also provide custom logic to parse the provided value into a number to be used in the filtering.
Custom number support is enabled by specifying configuration similar to the following:
const [columnDefs, setColumnDefs] = useState([
{
field: 'age',
filter: 'agNumberColumnFilter',
filterParams: {
// note: ensure you escape as if you were creating a RegExp from a string
allowedCharPattern: '\\d\\-\\,',
numberParser: text => {
return text == null ? null : parseFloat(text.replace(',', '.'));
},
numberFormatter: value => {
return value == null ? null : value.toString().replace('.', ',');
},
}
}
]);
<AgGridReact columnDefs={columnDefs} />The allowedCharPattern is a regex of all the characters that are allowed to be typed. This is surrounded by square brackets [] and used as a character class to be compared against each typed character individually and prevent the character from appearing in the input if it does not match (in supported browsers).
The numberParser should take the user-entered text and return either a number if one can be interpreted, or null if not.
The numberFormatter should take a number (e.g. from the Filter Model) and convert it into the formatted text to be displayed, or null if no value.
An allowedCharPattern of \\d\\-\\. will give similar behaviour to the default number input.
The following example demonstrates custom number support:
- The first column shows the default Number Filter behaviour.
- The second column demonstrates custom number support, and uses commas for decimals and allows a dollar sign ($) to be included.
- Floating filters are enabled and also react to the configuration of
allowedCharPattern.
Number Filter Model Copy Link
The Filter Model describes the current state of the applied Number Filter. If only one Filter Condition is set, this will be a NumberFilterModel:
Filter type is always 'number' |
The number value(s) associated with the filter. Custom filters can have no values (hence both are optional). Range filter has two values (from and to), where filter acts as a from value.
|
Range filter to value.
|
One of the filter options, e.g. 'equals' |
If more than one Filter Condition is set, then multiple instances of the model are created and wrapped inside a Combined Model (ICombinedSimpleModel<NumberFilterModel>). A Combined Model looks as follows:
// A filter combining multiple conditions
interface ICombinedSimpleModel<NumberFilterModel> {
filterType: string;
operator: JoinOperator;
// multiple instances of the Filter Model
conditions: NumberFilterModel[];
}
type JoinOperator = 'AND' | 'OR';
An example of a Filter Model with two conditions is as follows:
// Number Filter with two conditions, both are equals type
const numberEquals18OrEquals20 = {
filterType: 'number',
operator: 'OR',
conditions: [
{
filterType: 'number',
type: 'equals',
filter: 18
},
{
filterType: 'number',
type: 'equals',
filter: 20
}
]
};
Number Filter Options Copy Link
The Number Filter presents a list of Filter Options to the user.
The list of options is as follows:
| Option Name | Option Key | Included by Default |
|---|---|---|
| Equals | equals | Yes |
| Does not equal | notEqual | Yes |
| Greater than | greaterThan | Yes |
| Greater than or equal to | greaterThanOrEqual | Yes |
| Less than | lessThan | Yes |
| Less than or equal to | lessThanOrEqual | Yes |
| Between | inRange | Yes |
| Blank | blank | Yes |
| Not blank | notBlank | Yes |
| Choose one | empty | No |
Note that the empty filter option is primarily used when creating Custom Filter Options. When 'Choose one' is displayed, the filter is not active.
The default option for the Number Filter is equals.
When providing filter options, the default filter option (or the first option if no default set) must be an option that displays an input or the empty filter option (as a filter option with no inputs would mean the filter is active by default).
Range Input Validation and Error States Copy Link
When using the inRange filter type, the grid performs input validation to ensure the bounds of the range produce a valid filter; that is, where the start value is less than the end value.
Where this is not the case, the last edited input will display a red border and a hover tooltip directing the user to enter a valid value. While the filter is in an invalid state, the filter will not be applied. Screen readers that respond to the aria-invalid attribute or the ValidityState of the input will detect the input as invalid.
Number Filter Values Copy Link
By default, the values supplied to the Number Filter are retrieved from the data based on the field attribute. This can be overridden by providing a filterValueGetter in the Column Definition. This is similar to using a Value Getter, but is specific to the filter.
Function or expression. Gets the value for filtering purposes. |
Applying the Number Filter Copy Link
Applying the Number Filter is described in more detail in the following sections:
Blank Cells Copy Link
If the row data contains blanks (i.e. null or undefined), by default the row won't be included in filter results. To change this, use the filter params includeBlanksInEquals, includeBlanksInNotEqual, includeBlanksInLessThan, includeBlanksInGreaterThan and includeBlanksInRange. For example, the code snippet below configures a filter to include null for equals, but not for less than, greater than or in range (between):
const filterParams = {
includeBlanksInEquals: true,
includeBlanksInNotEqual: false,
includeBlanksInLessThan: false,
includeBlanksInGreaterThan: false,
includeBlanksInRange: false,
};
In the following example you can filter by age and see how blank values are included. Note the following:
- Column Age has both
nullandundefinedvalues resulting in blank cells. - Toggle the controls on the top to see how
includeBlanksInEquals,includeBlanksInNotEqual,includeBlanksInLessThan,includeBlanksInGreaterThanandincludeBlanksInRangeimpact the search result.
Data Updates Copy Link
The Number Filter is not affected by data changes. When the grid data is updated, the filter value will remain unchanged and the filter will be re-applied based on the updated data (e.g. the displayed rows will update if necessary).