Floating Filter Components allow you to add your own floating filter types to AG Grid. You can create a Custom Floating Filter Component to work alongside one of the grid's Provided Filters, or alongside a Custom Filter.
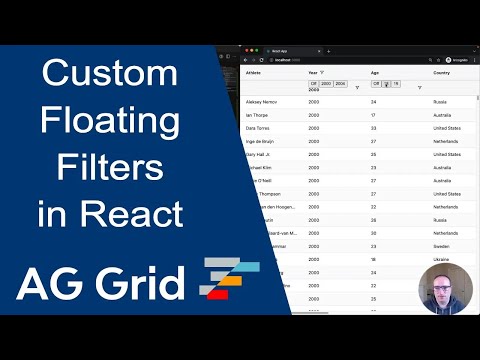
Example: Custom Floating Filter Copy Link
In the following example you can see how the Gold, Silver, Bronze and Total columns have a custom floating filter NumberFloatingFilter. This filter substitutes the standard floating filter for an input box that the user can change to adjust how many medals of each column to filter by based on a greater than filter.
Implementing a Floating Filter Component Copy Link
To configure custom floating filters, first enable the grid option enableFilterHandlers.
If you do not enable the grid option enableFilterHandlers, it is still possible to use custom floating filters, however this is not recommended. See Legacy Floating Filter Component.
Custom floating filter components are controlled components, which receive a filter model as part of the props, and pass model updates back to the grid via the onModelChange callback. A filter model of null means that no filter is applied (the filter displays as inactive). Note that the filter is applied immediately when onModelChange is called.
export default ({ model, onModelChange }) => {
return (
<div>
<input
type="text"
value={model || ''}
onChange={({ target: { value }}) => onModelChange(value === '' ? null : value)}
/>
</div>
);
}
Custom Floating Filter Parameters Copy Link
Floating Filter Props Copy Link
The following props are passed to the custom floating filter components (CustomFloatingFilterDisplayProps interface). If custom props are provided via the colDef.floatingFilterParams property, these will be additionally added to the props object, overriding items of the same name if a name clash exists.
The params object passed to the filter. This is to allow the floating filter access to the configuration of the parent filter. For example, the provided filters use debounceMs from the parent filter params. |
The current applied filter model for the column.
|
Callback that should be called every time the model in the component changes.
additionalEventAttributes If provided, will be passed to the filter changed event
|
Callback that can be optionally called every time the floating filter UI changes. The grid will respond with emitting a FloatingFilterUiChangedEvent. Apart from emitting the event, the grid takes no further action. The callback takes one optional parameter which, if included, will get merged to the FloatingFilterUiChangedEvent object.
|
Get the filter handler instance. If using a SimpleColumnFilter, the handler is is a wrapper object containing the provided doesFilterPass callback.
|
'init' | 'ui' | 'filter' | 'api' | 'colDef' | 'dataChanged' |
The column this filter is for. |
Shows the parent filter popup.
|
The grid api. |
Application context as set on gridOptions.context. |
Floating Filter Callbacks Copy Link
The following callbacks can be passed to the useGridFloatingFilter hook (CustomFloatingFilterCallbacks interface). All the callbacks are optional, and the hook only needs to be used if callbacks are provided.
Optional: A hook to perform any necessary operation just after the GUI for this component has been rendered on the screen. This is useful for any logic that requires attachment before executing, such as putting focus on a particular DOM element.
|
Example: Custom Filter And Custom Floating Filter Copy Link
This example extends the previous example by also providing its own custom filter NumberFilter in the Gold, Silver, Bronze and Total columns.
Example: Custom Filter And Read-Only Floating Filter Copy Link
If you want to provide a custom filter but don't want to provide an equivalent custom floating filter, you can implement getModelAsString() on the filter handler and you will get a read-only floating filter for free.
This example uses the previous custom filter but implements getModelAsString(). Note how there are no custom floating filters and yet each column using NumberFilter (Gold, Silver, Bronze and Total) has a read-only floating filter that gets updated as you change the values from the main filter.